For micro medical components, there is a wide variety of materials to choose from. Most micromolding materials fall into two categories: thermoplastics and bioabsorbables.
Thermoplastics are polymers that become pliable and moldable above a specific temperature and return to a rigid state upon cooling. They have long been used in the micromolding world.
Many new micro medical applications rely on bioabsorbable materials (also called resorbable, bioresorbable, or biodegradable) because the materials dissolve or absorb into the body, eliminating the need for additional surgeries and minimizing concerns about adverse effects. Devices made from these materials metabolize over time so secondary invasive procedures are not needed to remove them.
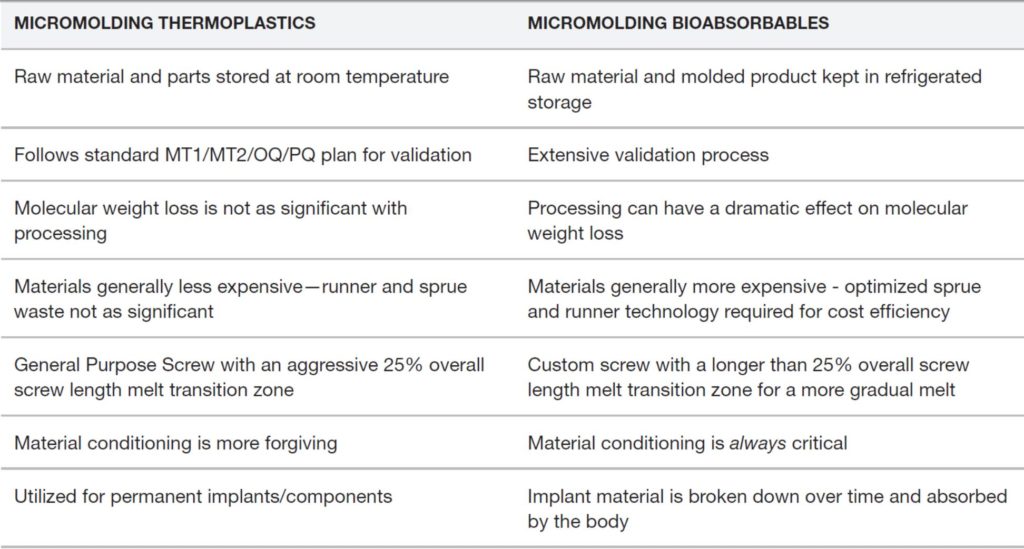
Across the board with plastics, the rules are different when you mold it so small. But when it comes to bioabsorbable resins, some molders assume that a thermoplastic material shares the same molding properties, so it is treated the same way. Bioabsorbables, however, require a much more extensive and specialized approach.
There are key differences between thermoplastic and bioabsorbable materials when it comes to handling, testing requirements, uses, and optimal processing conditions. Review a few of them in the table below: